Objective: Study of the enzyme kinetics for saccharification of starch using amylase enzyme.
Theory: Reaction of enzyme and substrate follows Michaeli’s Menten kinetics and is a two step reaction. In the first phase of reaction Enzyme (E) reacts with Substrate (S) to form ES (Enzyme-Substrate complex). This reaction is relatively fast and reversible in nature. The ES complex is, thereafter, decomposed to form product and enzyme is released. The above reactions can be written as follows –

The velocity (V) of above reaction is measured by rate of decomposition of ‘ES’ complex which is a slower reaction amongst the two reactions (1 & 2) described above. Velocity ‘V’ can be theoretically described by Michaeli’s Menten equation as shown below -
V = Vmax S / (Km + S)
Where, V = Reaction velocity
Vmax = Maximum velocity of Enzyme Substrate reaction
S = Concentration of substrate
Km = Michaelis – Menten constant.
The velocity of the reaction is experimentally measured by the measurement of rate of either the disappearance of substrate (ds/dt) or appearance of product (dp/dt). The variation of velocity of enzyme substrate reaction can be studied experimentally. For Michaeli’s Menten Kinetics the nature of ‘V’ vs ‘S’ plot appears as shown below –
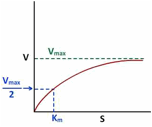
However it is important to note that Vmax is asymptote to the ‘V’ vs ‘S’ curve therefore it may be not be possible to find out the accurate value of Vmax from above plot with the result the Km measurement also will also be inaccurate.
A plot of 1/V vs 1/S (known as Lineweaver Burk Plot) is generally used for the accurate measurement of Vmax or Km. The slope of the above plot gives ‘Km/Vm’ while the intercept on ‘y’ axis gives ‘1/Vm’. Therefore the slope and intercepts together help in the calculation of enzyme kinetic parameters Vm & Km.
1/V = (Km/Vm) S + 1/Vm
Y = m X + C
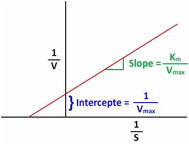
The value of ‘Vm’ & ‘Km’ are considered to be the key kinetic parameters for enzyme substrate reaction. For example ‘Vm’ describes the maximum permissible velocity of enzymatic reaction and ‘Km’ value reflects the affinity of substrate with the enzyme. For example the lower value of ‘Km’ indicates higher affinity of enzyme with substrate and vice versa.
Effect of temperature on the velocity of enzyme substrate reaction –
It has been indicated that velocity (V) of the enzymatic reaction is highly dependent on the reaction temperature. A study of ‘V’ vs Temperature (as shown below) is, therefore, essential to identify the right temperature of Enzyme - Substrate reaction for achieving highest velocity of reaction.
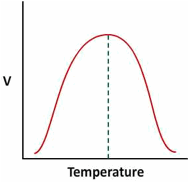
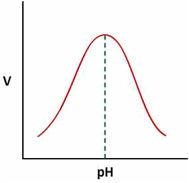
Effect of pH on the velocity of enzyme substrate reaction –
It has also been observed that velocity (V) of the enzymatic reaction is highly dependent on the pH of the reaction mixture. A study of ‘V’ vs pH (as shown below) is, therefore, essential to identify the right pH conditions for Enzyme - Substrate reaction for achieving highest velocity of reaction.