Objective: To study the batch growth kinetics and establish the key kinetic parameters
a) Maximum specific growth rate (μm) h -1
b) Saturation constant, (Ks) g.L-1
c) Overall yield of biomass (Yx/s) g cell. g-1 substrate
d) Dynamic yield (Yx/s) g cell. g-1 substrate
e) Overall productivity of biomass, g cell. 1-1.h-1
Culture Medium:
S. No. |
Medium Component |
Concentration (g.L-1) |
1. |
Glucose |
3.0 |
2. |
Ammonuim sulphate |
2.5 |
3. |
Na2HPO4 |
7.9 |
4. |
KH2PO4 |
3.7 |
5. |
MgSO4, 7 H2O |
0.625 |
6. |
NaCl |
0.625 |
7. |
CaCl2 |
0.019 |
8. |
Yeast extract |
0.125 |
Prepare 400 ml seed culture medium of the above composition. Take 200 ml medium each in two 500 ml flasks. Adjust the pH to 7.0 with NaOH. A mixture containing Glucose and CaCl2 is to be taken in one flask while the remaining medium components are taken in another flask. The above two flasks are sterilized separately and reconstituted in laminar hood only after cooling.
Acid/Base Solutions for pH control: Prepare 200 ml each of 1N HCl and 1N NaOH solutions in 500 ml flasks. Place cotton plugs and connect the silicon tubing for peristaltic pumps. Clamp the tubings and autoclave them.
Antifoam agent: Prepare 25 ml of a 5% suspension of silicon oil in poly propylene glycol (PPG) solution and sterilize in the autoclave.
Production Medium: The above medium recipe composition is also to be used for the bioreactor.
Procedure:
- A custom made empty flask having the transfer arm is to be used as an inoculum flask. Sterilize medium component flasks & acid / alkali flasks (for pH control) together in an autoclave.
- Dissolve the medium components in 500 ml distilled water (each) in two separate flasks one having glucose and calcium chloride and the other having the rest of the medium components Take adequate amount of distilled water to reconstitute the fermenter medium in the bioreactor and sterilize it separately in two liter flask.
- Autoclave the different flasks and the bioreactor vessel separately Asceptically transfer the medium in the bioreactor & add appropriate amount of sterilized distilled water aseptically to reconstitute the media Connect the acid / alkali flasks and the respective sterilized tygon / silicon tubes to the bioreactor. Also connect the chilled water supply to the bioreactor. Activate the pH & temperature controllers with the set point pH of 7.0 and temperature of 300C respectively.
- Set aeration rate to 1.0 vvm.
- Once the pH & temperature reaches the set point, the fermentor is ready for inoculation.
- Inoculate the fermentor with exponentially growing culture of E. coli.
Take samples every hour. Immediately take the Optical Density at 620 nm using a spectrophotometer. Calculate the biomass using the OD vs biomass correlation. For the measurement.
Observations: Tabulate your observations in the following table -
S. No. |
Fermentation Time (h) |
Glucose concentration |
Cell Mass |
1. |
|
|
|
2. |
|
|
|
3. |
|
|
|
4. |
|
|
|
5. |
|
|
|
6. |
|
|
|
7. |
|
|
|
8. |
|
|
|
9. |
|
|
|
10. |
|
|
|
Computations:
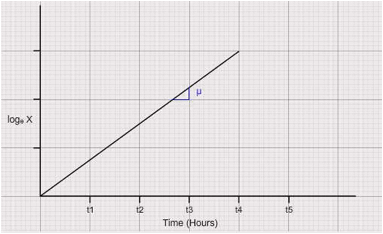
- Specific growth rate:
Ignore the lag period of the cultivation where in no increase in biomass is observed. Plot loge "X" vs "t" curve in the exponential phase of the growth. The slope of this curve is the specific growth rate of the culture.
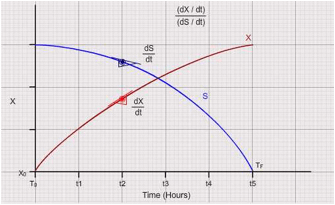
- Maximum specific growth rate and saturation constant:
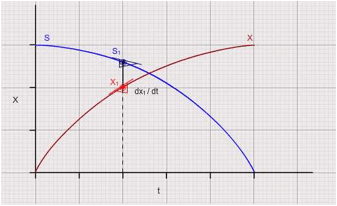
Plot "X" and "S" vs time curves. Select 5 points in the declining phase on the growth curve (reducing subtrate concertation). Draw tangents for "X" vs "t" curve to calculate "dX / dt". Identify the corresponding values of "S" at the same points which were used for making the tangents and consolidate the data in the following table (Please see the graph for detailed explanation) :
Time |
S |
X |
dX / dt |
μ[(1/X)*(dX/dt)] |
1/ μ |
1/S |
1. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
3. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
4. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
5. |
|
|
|
|
|
|
Plot "1 / μ" vs "1 / S". Fit a linear regression line through the data points.
Assuming the applicability of Monod’s Equation µ = µmax S / (KS + S)
Therefore 1 / µ = ( KS / µmax ) 1 / S + 1 / µmax
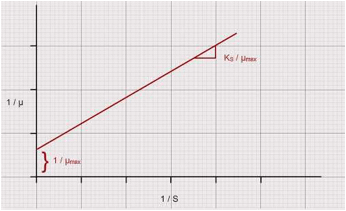
The slope of above line = (KS / µmax) and the intercept (1/ µmax) on abscissa = (1/μm). From these compute the values of "μm" and "Ks".
- Overall growth yield coefficient:
Figure out the total biomass produced out of the entire substrate as shown in the figure:
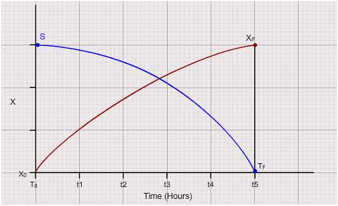
It is computed as the ratio of tangents to the biomass curve and substrate curve i.e., (dX / dt ) / (dS / dt) at different time intervals. To compute overall productivity of biomass calculate (XF – XO) / (TF – TO).