Objective: To estimate volumetric mass transfer coefficient (KLa) by oxygen balance method.
Theory: For a well aerated and agitated culture growing in a bioreactor when air is sparged in the fermentation broth of a bioreactor a part of the oxygen present in the incoming air is dissolved in the liquid from which the microorganisms in the system receive oxygen for their respiration and metabolic activities, the unabsorbed oxygen goes out through the exit gas under highly agitated or strong air conditions. Therefore a net balance with respect to oxygen can be written as:
![]()
![]()
![]()
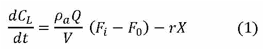
![]()
![]()
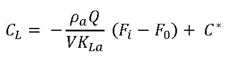
![]()
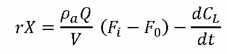
Since ![]() is very small quantity compared to the first term on the RHS of above equation. It can be neglected
is very small quantity compared to the first term on the RHS of above equation. It can be neglected
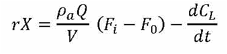
Therefore the demand of the oxygen by the growing cells can also be calculated.
Advantages: In dynamic method (for KLa measurement) perturbations are given to the growing culture during the cultivation (For example air is switched off and turned on again). These interruptions during the cultivation should be avoided as far as possible as it may lead to instantaneous mutation. In Oxygen Balance method the KLa measurement is done in actual cultivation condition with-out any interruptions to the system.